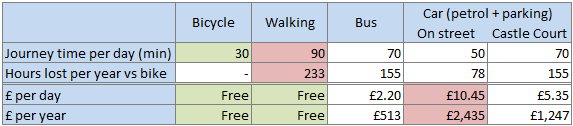
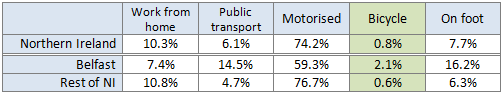
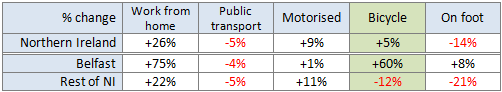
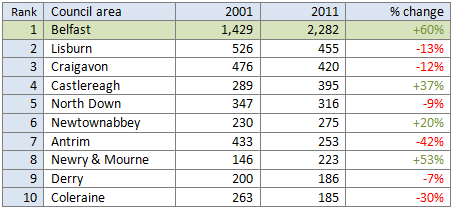
The North Down Coastal Path, and the surrounding local economy, is one major project away from fulfilling its tourism and leisure potential. A new high quality traffic-free link is needed to address the current disconnection from Belfast. This will integrate with the growing urban greenway network, encourage Belfast residents to visit North Down more regularly, and open up a new seam of tourism opportunities. Considering the current options for route development, an intriguing new greenway project is proposed.

.
The North Down Coastal Path begins at the north end of the George Best Belfast City Airport runway, with a gate to the road running past the Kinnegar Army base. From here, Belfast City Hall is 6.5km away with no direct traffic-free route. When the Connswater Community Greenway is completed as far as Victoria Park the shortest distance to this pathway network will be 4.5km, but accessible only by busy main roads.
This is a particular problem for leisure cycling; families with youngsters, inexperienced cyclists, tourists based in Belfast. These are already significant distances before the relaxed ‘leisure’ part begins, and poses a barrier to many people who would otherwise love to tootle along the coast for a day and spend in the local economy.
At present there are just two options available for travelling by road. Both routes are quite direct, but also have severe drawbacks for cycling and walking.
The A2 / Sydenham Bypass
The road ‘benefits’ from separate cycle tracks on both carriageways, but you’ll seldom see people choosing to take this route. This is quite a horrible place to be on a bicycle; a heavy traffic urban dual carriageway, with vehicles travelling above and below the 50mph speed limit.
An apparent lack of sweeping leaves the cycling surface strewn with road grit and glass. Not a happy start or end to a leisure trip, and not somewhere suitable for children or inexperienced riders to cycle. Great if you like cinematic thrills, but not fit for purpose as a modern cycle route.

It’s hard to imagine a country like the Netherlands, where road design is based on sustainable safety principles, funnelling cyclists into the hard shoulder of what is practically an urban motorway, then promoting it as an important link in the country’s cycle network.
Pedestrian access to the bypass is slightly easier with the footbridge at Sydenham Station and subway by Victoria Park, but the drawbacks of the traffic noise and fumes make this a less than appealing environment. Popular with joggers and power walkers, but lacking in great utility.
Future development of the road will include widening to three lanes each way. There will be just one 3.5m shared cycle/footway on the Victoria Park/Airport side – finally to include a physical barrier which should improve safety perception – but designing a mixed footpath on this fast cycling commuter route is a real backward step.
As the Sydenham Bypass reaches the Tillysburn Gyratory, it’ll be back to the current heady mix of footpaths, hard shoulders and crossing over fast slip roads. With no cycle lane up the slip road to Holywood Exchange, cyclists are encouraged to continue for another 2.6km on the dual carriageway into Holywood town, missing the first section of coastal path.
While it’s important to retain cycling and walking space in major road developments, this appears to be an ideal time to seek better accommodation for sustainable journeys on this corridor.
The Airport Road
Favoured by many cyclists at present, the Airport Road tracks the western side of George Best Belfast City Airport. By comparison with the Sydenham Bypass, the traffic flows are greatly reduced. Yet heavy goods vehicles and oil tankers dominate the road here, and again this poses a frightening dilemma for the novice cyclist. The pathways suffer from high kerbs and no dropped access at the many side roads; unsuitable for cycling, so the road is the only option at present.
There are plenty of opportunities on the countrybound side to reclaim space to develop a separate cycle track with the parallel pedestrian pavement. This is understood to be the preferred solution for a future cycling route, with a new bridge due to link Victoria Park with the Airport Road at the end of the Connswater Community Greenway.

Yet there is another issue which makes this route currently unattractive – the isolation. There is one way in and one way out, with some limited added value with the commuting link to the Bombardier site and businesses based in the Heron Road Complex. But workers here will tell you the dirt left by heavy construction traffic makes cycle commuting conditions less than ideal.
The Airport Road option also narrows the usefulness of the route to cyclists only. Very few ‘additional’ walking journeys would be generated along this stretch, being set so far away from residential areas.
But is there another way to accommodate sustainable transport in this part of the city, and link the greenway networks, away from the compromises of being tied to major roads?
A Sydenham Community Greenway?
Looking to the southeast side of the airport, across the A2 and railway line, there is another option worth exploring which ticks many more boxes:
- direct route
- traffic-free
- space for full mode separation where needed
- integration with rail network
- greater number of access points
- weaving through residential communities
- integration with existing leisure facilities
- new commuting and shopping access

Starting from the Connswater Community Greenway link to Victoria Park, this route would make use of Inverary Drive. This traffic-calmed and relaxed residential road is an ideal start, running for almost a full kilometre. There is an existing bridging pathway between Park Road and Inverary Drive which can be upgraded to greenway standard.

Inverary Drive is a wide and calm street environment with very little through traffic. It’s possible to accomodate cycling on the road (with a 20mph limit) but space exists to provide a fully separate track by the railway fence for a ‘continuous’ route feel, and providing the highest safety standard to separate pedestrians, cyclists and other vehicles for this short stretch.

There is an important link with Sydenham railway station on this route, and a greenway route on the doorstep opens this station up as a jumping off point for journeys towards the Connswater/Comber corridor, and north where we’re headed.
Continuing on, the road turns east into Inverary Avenue at the Inverary Community Centre, but this proposal would run a traffic-free path behind the centre and through Alderman Tommy Patton Memorial Park. This popular urban park has recently upgraded its play facilities, and is another lesser-known gem in Belfast. Passing by the football pitches, the new path would approach a patch of woodland. There is an existing looped forest pathway which runs along the boundary with the train line; this could be carefully and respectfully upgraded for the purposes of a continuous greenway route.

Viewed from the woodland path, the potential local benefits of the next section start to snowball – the main terminal of George Best Belfast City Airport is but a stone’s throw away. The greenway would continue to follow the line of the railway fence, across the back of Shorts Recreation Club and Blanchflower Park.

As with Alderman Tommy Patton Memorial Park, there appears to be ample space to set the railway fence back closer to the line if it’s necessary to accommodate the path away from the existing parks. But for the whole route to be viable, one piece of major engineering is needed at this point.

The most direct route to Holywood requires the path to cross over the railway lines opposite the airport. There are two options here:
- a standalone bridge crossing diagonally to meet the airport exit road
- a looped ‘S’ bend crossing over the railway tunnel at the Sydenham Bypass and turning again into the airport exit tunnel

A simple upgrade of the airport access tunnel can continue the route towards Holywood Exchange. The tunnel already has a wide footpath and cycle lane marked on the road. Providing kerb separation at the exiting cycle line would allow 2-way cycling and walking without affecting airport traffic. There is a further option to drop an access path from the countrybound Sydenham Bypass, allowing direct cycling and walking access from the Tillysburn cycling underpass and linking the communities around Knocknagoney Park.

The City Airport site employees around 1,500 people, with many workers travelling from East Belfast with little option but to drive. This new greenway option opens up a significant swathe of Belfast to a truly viable alternative to car travel. And if you think the suggestion of cycling to an airport for onward travel is daft, this isn’t the case at other airports around the world, even including many served by George Best Belfast City Airport flights.

The roundabout at the airport tunnel leads off to an abandoned access road. Today this is used for fly tipping and is a favourite spot for taxis wanting to beat the waiting restrictions within the airport car parks. This is ripe for conversion to a walking and cycling-only route into the Harbour Estate at Holywood Exchange as part of the greenway. The proposed path would cut left alongside the airport boundary fence and into the retail complex at IKEA’s massive sign. There is already a natural land buffer between the airport boundary fence and Airport Road West, ripe for a separate cycle track all the way to the North Down Coastal Path.

Hundreds more local workers travel to the large businesses situated here: IKEA, Decathlon, B&Q, Sainsburys, Next, BHS, Harvey Norman. Commuting options are increased for locals, but also new options for shopping trips..
Cough cough .. stop right there! Shopping at IKEA? By bike?!
If the idea of cycling to IKEA to go shopping seems even more daft than the airport link, it’s perfectly obvious, natural and not uncommon in other countries. The difference between a city like Copenhagen and Belfast is exactly the type of traffic-free infrastructure being proposed here.
The separate cycle pathway would continue along the airport boundary fence until passing out of the Holywood Exchange complex, before turning under the flight path at the end of the runway. This is another one of those little treasures of Belfast – standing under a landing aircraft seemingly at touching distance.
Getting from the airport side to the Kinnegar gates requires a road crossing – the only one on this entire 4km route. The bulk of traffic on the road only goes as far as the retail park, so a pelican crossing beyond B&Q could be an appropriate solution. Once the confusing access issues with the Habour Tillysburn gates are ironed out, a continuous link to the North Down Coastal Path is now achieved.
Local value of a long-distance greenway
Running the connecting greenway through a residential community rather than the Airport Road must be carefully weighed. The main local benefit would be the potential displacement of some regular private car journeys to cycling and walking.
The 3 wards surrounding this proposed route, Sydenham, Island and Belmont, have just over 16,000 residents. Census figures bear out that these ‘greenway wards’ are not much different from the rest of Belfast; just shy of a quarter of all commuting journeys are under 2km (1.2 miles) and nearly two thirds within 5km (3 miles) range. Yet motorised trips are higher here at 56% (48% all Belfast) and walking journeys lower at 17% (22% all Belfast). One third of households in the greenway wards have no access to a car, which is a high figure in itself, but less than the Belfast average (40%), so the area is possibly more car dependant that it needs to be.

While the footprint of the proposed greenway is on the periphery of the residential area in these wards, it would still open up new linkages into the harbour estate and enhanced traffic-free sections for many parents and children on the school run to Victoria Park Primary School, Ashfield High Schools and Sandbrook Nursery School.
A potential new community greenway for Belfast, linking the city with the North Down Coastal Path, providing viable commuting, shopping and leisure alternatives to private car travel. On the face of it would seem a very cost-effective option should Belfast City Council, Northern Ireland Government departments, Sustrans or others wish to take it forward with a feasibility study. With just a few wrinkles to be ironed out on access, this would seem to provide excellent value for money – a 4km Sydenham Community Greenway as the final piece of a fully connected Belfast Metropolitan Area greenway network. Is it possible?















 But instead of being deterred, we need to organise and innovate! Since I started blogging about Belfast cycling I’ve seen amazing resourcefulness and passion among local people who choose to get around by bike. New community connections are being built every day, and spawning innovative action such as Reclaim Belfast’s Cycle Lanes 1 and 2. It is among the people who ride our streets every day that we will find creative solutions to change the experience and perception of cycling here.
But instead of being deterred, we need to organise and innovate! Since I started blogging about Belfast cycling I’ve seen amazing resourcefulness and passion among local people who choose to get around by bike. New community connections are being built every day, and spawning innovative action such as Reclaim Belfast’s Cycle Lanes 1 and 2. It is among the people who ride our streets every day that we will find creative solutions to change the experience and perception of cycling here.